Inconsistencies in data across different systems in an organization can have catastrophic consequences. Any mismatch or error will complicate data integration efforts and create integrity issues ultimately impacting the accuracy of business intelligence (BI), enterprise reporting, and analytics applications.
If data errors are not identified on time and fixed, it will cause a cascading effect on all other reports. Today, businesses have understood the consequences of mishandling data. Efforts to implement a well-rounded governance strategy will not only mitigate potential risks but also empower data to fetch the best outcome.
According to Forbes, data governance challenges are not limited to the way organizations collect data. They also arise from the differences in the manner a company and its employee consume data.

Objectives of Data Governance
Data governance helps organizations to analyze their data usage practices and gauge risks. As a result, audit measures, updating back-ups, and investigating audit issues become a priority. This system of governance ensures that data-driven decisions are made based on sound principles, adhering to ethical standards, and protecting the rights of those who are affected by their use.
Overall, the process of data governance standardizes data definitions across an enterprise or organization while other goals depend on the focus of a particular data governance program. Businesses can establish principles relevant to their specific environment based on commonly accepted data governance framework. Here are some fundamentals.
- Integrity is key. All resources need to be honest and forthcoming about constraints, challenges, and other impacts of data governance decisions.
- Establishing clear and transparent processes for both parties – participants and auditors about how practices and controls will be introduced and implemented.
- Enterprises should audit their data governance activities and support them with due documentation. This will help meet the requirements of compliance-based and operational audits.
- Cross-functional and data-related decisions, processes and controls need to be clearly defined so that it will be easier to determine and fix responsibility and accountability.
- Knowledge of how to assign, and delegate governance stewardship activities for both individual contributors and data stewardship groups.
- There has to be a checks and balance system between various teams in an organization or any person who uses/manages information.
- Actively support both proactive and reactive change management activities throughout all stages.
- The primary focus of a data governance program should be on the introduction and support of standardizing enterprise data.
Gemini Consulting & Services can help enterprises to plan a suitable data governance framework. Contact us to reduce data risks and make data-driven decisions that can improve the efficiency of an enterprise.
Once the organization works with the above, it is essential to pay attention to the following areas of potential hurdles.
- Businesses must integrate data governance with IT policy. Both need to work in tandem with each other for successful governance. Organizations cannot view data governance and IT policy separately.
- Employee cooperation and executive program buy-in can be a bit of a challenge. Users may need incentives and motivation to follow the new data governance initiatives. However, this needs a top-down buy-in from executives to create company-wide adoption.
- Data governance efforts need to pay attention to team needs and they should be simple to use. Most importantly, it needs to align work efforts with business goals. It is essential to make governance simple and flexible so that it is not viewed as an impediment.
- Selecting the governance technology platform and taking help from an expert can make this exercise less complicated and time-consuming.
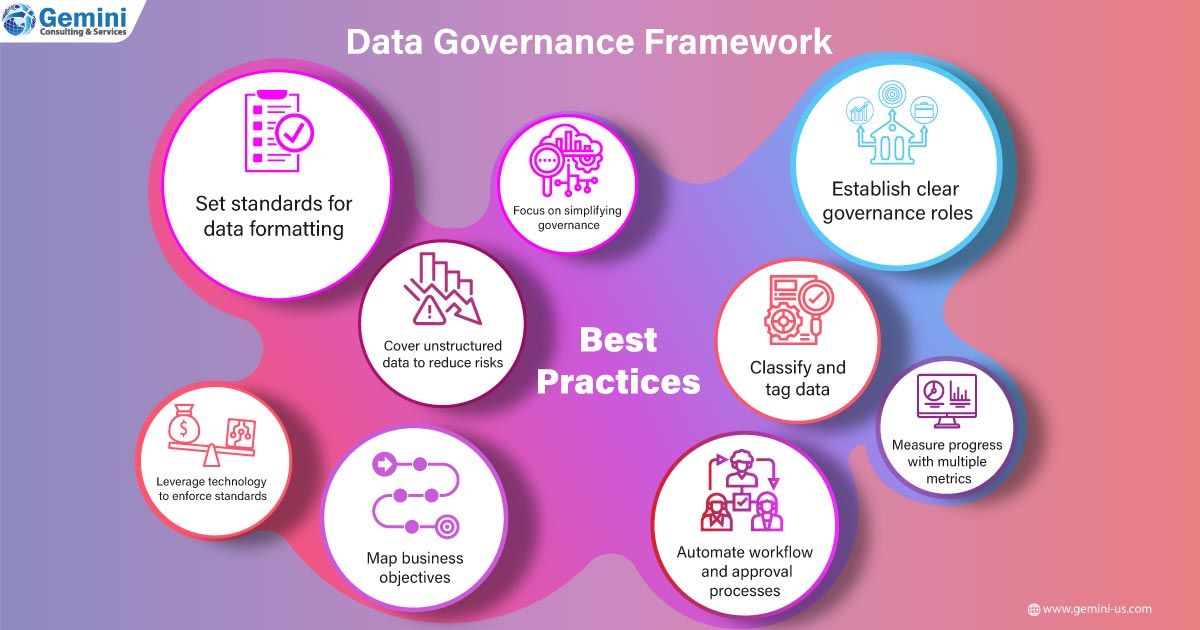
- Setting format standards for data and leveraging technology to enforce those standards is crucial. This helps with data ingestion and processing into the big data platform. Let us remember that data will be pulled from many disparate sources, and hence data normalization is key.
- A clear account for unmanaged data is to be set aside for data in files, folders, and shared data. This valuable data is usually much more at risk than the regular managed data. The data governance strategy also needs to cover unstructured data.
- Business goals need to be mapped for governance as early as possible with an assigned officer. Now this person will be responsible for managing and achieving the data governance goals. While the big picture needs to be kept in mind, creating manageable touchpoints along the way is important too.
- Focus on simplicity to minimize the impact on individual contributors and teams to pave the way for best practices to be easily followed.
- Since data owners are closest to the data they create and manage, it is advised to establish clear governance roles for teams. Data managers must work in tandem with data owners for guidance and to facilitate communication. Enterprises must set up cross-functional teams and empower them to implement data governance practices.
- Classify, tag data, and establish standards for metadata that promote business goals and allow for data reuse. It is important to standardize focus areas of data governance.
- Progress needs to be measured with multiple metrics, including a few key ones for data governance on stale data saved, folders assigned, and sensitive data created.
- Automating workflows, approval processes, data requests, and permission requests will help accelerate data governance initiatives. This not only helps save time and resources but also ensures governance implementation in a systematic manner.
A good data governance platform ensures that customer or employee information remains secure. It also enables an organization’s ability to capitalize on its own datasets. This is done by helping them leverage analytics capabilities such as descriptive analytics or predictive analytics. It ensures adequate protection of the needs of business stakeholders in the event of data leakage, data security, etc.



