Scores of business data generated are vulnerable to external threats. The fluid /hybrid nature of operations post the pandemic has accentuated the risks with customer interaction points and device agnostic access being extended due to remote work. Hacking, insider threats, natural disasters, and human errors are some of the main reasons for data security breaches and this mostly results in financial losses, compromised identities, and reputation damage.
According to Statista, in 2022, the average cost of a data breach in the financial industry worldwide was $5.97 million, up from $5.72 million in 2021. The global average cost of a data breach across all studied industries was $4.35 million, up from $4.24 million in the previous year.
All organizations irrespective of the nature of their business, size, and IT infrastructure are at risk of data security breaches. Here are the top 5 data security threats.

- Password reuse for emails and applications: Hackers take advantage of weak passwords. Business data is stored in different accounts and services are protected with just login credentials and therefore, strong unique passwords are important. Enterprise users can take advantage of password manager applications for the same.
- Improper data access control: The principle of the least privilege ensures that employee access to data is based mainly on their role and responsibilities. Allowing everyone in the company to access all data eventually lead to security compromise on critical and sensitive data like customer information, financials, acquisition plans, etc.
- Skip data backup: A frequent backup strategy is essential particularly to protect financial data, intellectual property, source codes, and email. Before anything, it is imperative to start by backing up mission-critical data.
- Failure to educate employees on common threats: Apart from human error, the bigger worry is phishing tactics and other popular scams used by hackers to entice users. Businesses need to invest in cybersecurity education programs for employees and teach them to perform without jeopardizing sensitive data.
- Absence of a dedicated security team: Data security demands a budget to help set up a dynamic team that can monitor traffic and detects anomalies. Outsourcing security to service providers with the specialized knowledge to properly configure and keep systems and applications safe is a good idea.
Data Governance and cybersecurity work together to protect valuable data assets and ensure that there is access to high-quality data as applicable. Protecting data and addressing cyber security threat are the main objectives of cybersecurity technology. Data governance complements this objective by pinpointing high-value and high-risk data sets and allocating specific resources to protect data. The evolving threat landscape and data privacy regulations have made data governance integral to organizations providing consistent protection from cyber attackers.
Data governance on AWS Cloud
Data governance is a principled approach to managing data that clearly outlines policies, procedures, responsibilities, and controls for data activities. This program ensures that information is collected, maintained, used, and disseminated systematically to ensure the organization’s data integrity and security needs are adhered to.
Privacy, security, access and quality are the main pillars on which data governance guidelines rest. Covering the roles and responsibilities of those implementing policies and compliance measures. These guidelines empower employees to access and use data and improve their potential.
Cloud governance allows enterprises to define and apply policies centrally and control costs. Gemini Consulting & Services can help enterprises to implement a cloud governance plan to protect the integrity and privacy of information. Contact us to understand the security features offered by AWS cloud governance and their advantages.
An Ideal Data Governance Practice
- Is a framework that helps users define, agree to, and enforce data policies.
- Uses effective processes to control, oversee and direct all data assets across on-premises systems, cloud, and data warehouse platforms.
- Determines the right tools and technologies that ensure data policy compliance.
An intuitive data governance solution that can extend across both on-premise and cloud data, safeguards a business from security threats and helps derive more value from such data. The AWS cloud governance framework is based on four key aspects – visibility, configuration, operations, and risk.
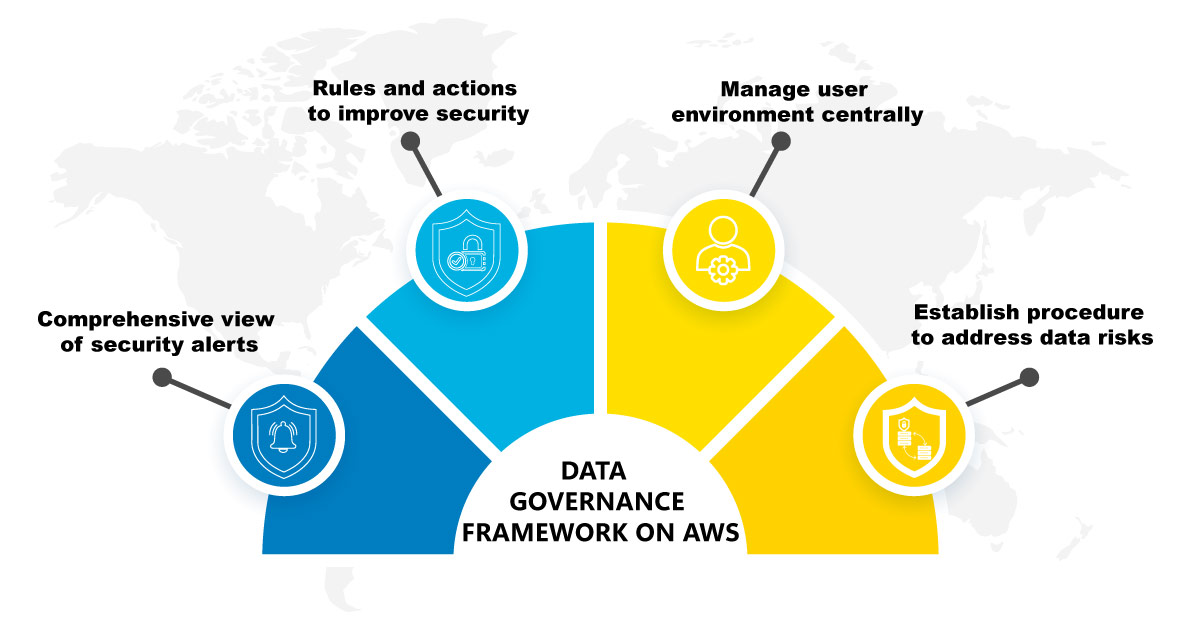
Visibility
This ensures an accurate and detailed view of all activities in the cloud environment of the business covering AWS accounts, stored data, cloud applications, platforms, users, and data accessed. The business faces data management issues in hybrid and multi-cloud environments, where unmanaged security issues can easily spread. In a practical scenario, when users or departments utilize hardware, software, and/or services without the knowledge of the company’s IT department.
- AWS Security Hub highlights security alerts from various SWA services, thus providing a comprehensive view of a company’s security posture.
- Amazon GuardDuty monitors activity to detect threats and unauthorized behavior.
- Amazon Macie uses ML to discover and protect sensitive data.
- AWS CloudTrail enables monitoring of logging and account activities. It provides a comprehensive event history that helps with troubleshooting and security analysis.
Configuration
The configuration usually is interpreted as misconfiguration, which represents an error that violates a company’s policy or that leads to user behavior impacting security. This happens for instance when an unauthorized user gains access to sensitive data or system settings. This is more in regulated industries like finance and healthcare.
- AWS Foundational Security Best Practices help businesses recognize deviations from security best practices and provide a guide to improving security.
- AWS Config Conformance Packs is a collection of rules and actions used to assess an AWS environment.
- AWS IAM Access Analyzer enables businesses to uncover unintended access to data.
Operation
As companies scale up their investment in the cloud, the processes used to manage the various activities become less suited for the task. The following features allow enterprises to handle this better.
- AWS System Manager allows businesses to view data from multiple AWS services and automate operational tasks.
- AWS Control Tower helps set up a safe multi-account AWS environment.
- AWS Organizations is used to centrally manage a user environment.
Risk
Risk encompasses all types of risks, such as financial, regulatory, data security, etc that can damage an organization. Therefore, every organization needs to establish processes to find and address security risks. With AWS services enterprises can have the following features to manage these risks.
- AWS Audit Manager enables managers to evaluate whether business activities and procedures are efficient.
- AWS Config is help enterprises to gauge and evaluate AWS resource configurations.
With cloud governance, a cloud can be broken down into smaller blocks each of which represents projects or departments. This improves visibility and cost control and reduces the impact of security problems.



