In today’s business landscape, Artificial Intelligence (AI) holds a significant presence across various critical functions, including customer service, sales, marketing, supply chain, manufacturing, finance, and human resources. Embracing AI can lead to substantial improvement in operational efficiency and provide businesses with a competitive edge.
By the year 2024, Gartner anticipates that 50% of new cloud-based system deployments will rely on a cohesive cloud data ecosystem rather than disparate point solutions. Gartner advises organizations to assess data ecosystems based on their capacity to address distributed data challenges and seamlessly integrate data sources beyond their immediate environment.
The success of AI hinges on multiple factors, but its primary foundation rests upon how companies gather, manage, and utilize data. Through a comprehensive approach to effective data management, AI can be employed as a solution capable of yielding significant business outcomes.
It’s important to recognize that AI is a multidisciplinary field, amalgamating data engineering, data sciences, DevOps, platform skills, and business acumen. Subpar data quality has the potential to detrimentally impact the precision of AI system predictions and decision-making, thereby, constraining favorable business outcomes. AI algorithms can inadvertently perpetuate existing biases present in the data, influenced by user knowledge and established processes.
Despite the availability of quality data, numerous companies grapple with vast datasets that are either difficult to access or remain siloed in disparate systems. Privacy and security concerns further compound this challenge, as businesses strive to safeguard data to prevent breaches and ensure ethical AI use. Underperforming AI tools can disappoint stakeholders and customers alike, leading businesses to reconsider investments and potentially abandon AI initiatives altogether.
In essence, imperfect data can severely dent revenues by generating unreliable results.

Constructing a Robust Data Framework
To meet the demands of generative AI, a mindful approach to handling data, encompassing transaction records, analytics, code, and proprietary information, is imperative. Algorithms must be empowered to discern patterns for predictive capabilities, and operational data should be consolidated within a centralized data lake. This strategy facilitates the creation of expansive language models, enabling a coordinated and comprehensive approach to data management across the organization.
Ensuring data quality through proper formatting, organization, and relevance is pivotal for effectively training AI models. Sound formatting, organization, and relevancy of data are fundamental for yielding meaningful results. Data governance is vital, requiring productive collaboration with risk management staff to define access privileges and establish usage policies.
AI is here to stay and is slated to grow more powerful and valuable for the foreseeable future. To harness the most of this technology and its growing capabilities, partner with Gemini Consulting & Services. Organizations need to focus now on building the solid data foundation that AI needs to push the business forward onwards and upwards. Struggling to handle your business data? Contact us.
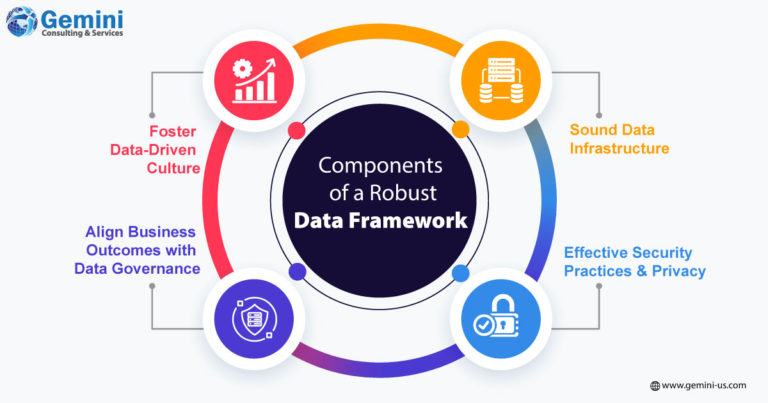
Fostering a Data-Driven Culture: Encouraging data-driven decision-making while discouraging guesswork is essential. Equipping employees with the necessary tools, data, and training to make informed choices accomplishes this goal. Establishing clear guidelines for sending data to AI systems, maintaining a separation between sanctioned and research data, and monitoring usage cases are critical. Likewise, ensuring the security of off-limits data sets is imperative for controlled access.
Aligning Business Outcomes with Data Governance: Governance efforts must be directly connected to the business strategy and priorities and hence clear policies and procedures to consume data need to be laid down. This must also include accountability and decision rights related to data use. It is also necessary to maintain an audit trail of all corporate data being fed into AI applications.
A Sound Data Infrastructure: The necessary infrastructure, tools, and skills are to be available to manage and analyse data effectively and ensure it is complete, relevant, consistent, organized, and readily available for consumption. Data warehouses and lakes data monitoring and remediation tools, and data visualization tools, need to be implemented along with the necessary hardware and software. A well-structured data infrastructure can help businesses swiftly adopt and leverage large language models customized to handle contract management, customer service, and code generation.
Effective Security Practices and Privacy: Robust security practices help protect data from unauthorized access or misuse. A formal mechanism ensures compliance with relevant privacy regulations and their dynamics. The businesses must be able to track commissioned derivative works from generative AI tools and how they are used internally and externally, to protect against any lawsuits for copyright infringement.
How to Do Data Management?
Businesses need to first assess data assets and go on to understand likely liability issues pertaining to data inclusion in AI. It is important to research vulnerabilities, limitations, etc offered by an AI tool before implementing it. Needs and top use cases can also be discovered and as such goals will help determine the right AI solution. It is possible that not all projects are suited for generative AI. Businesses can also consider software tools that can help filter outcomes by objectionable or inaccurate data sources and monitor the security and privacy risks of data. This helps avoid leakage or privacy violations; teams can move to private sandbox environments for experimentation.
In conclusion, effective data management stands as the cornerstone for extracting maximum value from generative AI. Its implementation is pivotal for accurate predictions, meaningful results, and ultimately, achieving a competitive edge in the AI-driven business landscape.



